Blogs
If you’re a BI professional struggling to get clarity on different types of data models, then this comprehensive guide is all that you need to study. In our previous blog, “The Data Modeling Beginner’s Guide for 2025”, we discussed how Data Modeling forms the backbone of efficient data management. However, not all data models are created equal. Let’s delve deeper.
Types of data model
As a BI professional, it’s crucial to understand the different types of data models to create structured and scalable systems. Let us understand each data model type and their roles in data architecture.
1. Relational Data Model
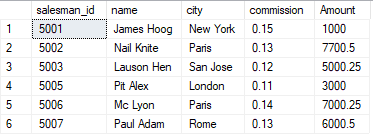
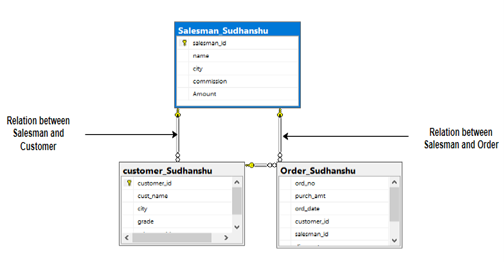
A Relational Data Model consists of a collection of tables, each of which is assigned a unique name. Relational Database generally uses a query language, similar to SQL, for data management.
Consider a relation Salesman with attributes Salesman_id, name, city, commission, and Amount shown in the table.
Let us suppose we have 3 relations.
2. Entity-Relationship Model (ER Model)
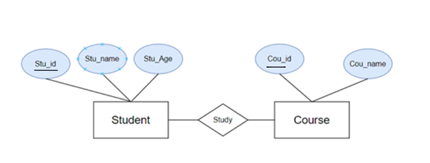
An Entity-Relationship Model represents the structure of the database with the help of a diagram. ER Modelling is a systematic process designing a database as it would require you to analyze all data requirements before implementing the database.
For example, suppose we design a school database. In this database, the student will be an entity with attributes like Stu_id, Stu_name, Stu_Age, etc. The Course can be another entity with attributes like cou_id, Cou_name etc. and there will be a relationship between them.
Components of an ER model :
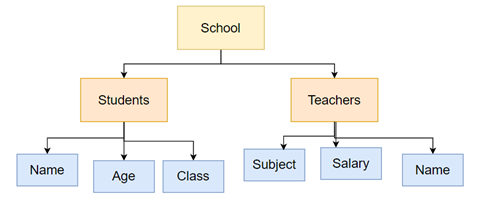
3) Hierarchical Data Model
A hierarchical data model is a data model where data is arranged in a tree-like structure. Each piece of information is stored as a record and is linked to one another through links. A record is a collection of fields, and each field contains a single value. The type of record decides what information is included in it. This way, it forms a structured and organized way of storing and connecting data.
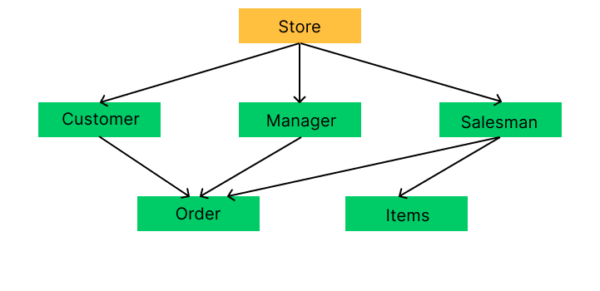
4) Network Data model
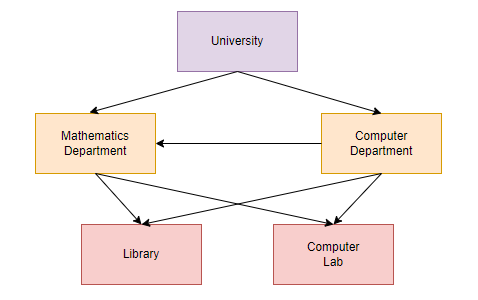
The network database model was developed to address the limitations of the hierarchical database model. Unlike the hierarchical model, this approach allows a child to be associated with multiple parents. In this model, parent nodes are referred to as owners, and child nodes are designated as members.
As mentioned, graphical representation “University” will be a Parent and Mathematics Department will be Child.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data modeling proves to be very crucial when it comes to data management as it guides us in designing efficient and scalable databases. By understanding the various types of data models such as the Relational Data Model, Entity-Relationship Model, Hierarchical Data Model, and Network Data Model, we discover the strengths and weaknesses of each, which ultimately helps us in deciding its application and suitability for different scenarios. Data management is ever evolving, and it is possible only through knowledge to make informed choices regarding the performance of any application and harness its potential to the fullest.